728x90

HTTP Response Header
1. Response Status
response.setStatus(번호);
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
response.setStatus(200); //성공
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK); //200 성공
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST); //실패 400
HttpServletResponse 클래스에서 응답상태 코드를 볼 수 있다.
📑 HttpServletResponse
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
/**
* Extends the {@link ServletResponse} interface to provide HTTP-specific
* functionality in sending a response. For example, it has methods to access
* HTTP headers and cookies.
* <p>
* The servlet container creates an <code>HttpServletResponse</code> object and
* passes it as an argument to the servlet's service methods (<code>doGet</code>, <code>doPost</code>, etc).
*
* @see javax.servlet.ServletResponse
*/
public interface HttpServletResponse extends ServletResponse {
/**
* Adds the specified cookie to the response. This method can be called
* multiple times to set more than one cookie.
*
* @param cookie
* the Cookie to return to the client
*/
public void addCookie(Cookie cookie);
/**
* Returns a boolean indicating whether the named response header has
* already been set.
*
* @param name
* the header name
* @return <code>true</code> if the named response header has already been
* set; <code>false</code> otherwise
*/
public boolean containsHeader(String name);
/**
* Encodes the specified URL by including the session ID in it, or, if
* encoding is not needed, returns the URL unchanged. The implementation of
* this method includes the logic to determine whether the session ID needs
* to be encoded in the URL. For example, if the browser supports cookies,
* or session tracking is turned off, URL encoding is unnecessary.
* <p>
* For robust session tracking, all URLs emitted by a servlet should be run
* through this method. Otherwise, URL rewriting cannot be used with
* browsers which do not support cookies.
*
* @param url
* the url to be encoded.
* @return the encoded URL if encoding is needed; the unchanged URL
* otherwise.
*/
public String encodeURL(String url);
/**
* Encodes the specified URL for use in the <code>sendRedirect</code> method
* or, if encoding is not needed, returns the URL unchanged. The
* implementation of this method includes the logic to determine whether the
* session ID needs to be encoded in the URL. Because the rules for making
* this determination can differ from those used to decide whether to encode
* a normal link, this method is separated from the <code>encodeURL</code>
* method.
* <p>
* All URLs sent to the <code>HttpServletResponse.sendRedirect</code> method
* should be run through this method. Otherwise, URL rewriting cannot be
* used with browsers which do not support cookies.
*
* @param url
* the url to be encoded.
* @return the encoded URL if encoding is needed; the unchanged URL
* otherwise.
* @see #sendRedirect
* @see #encodeUrl
*/
public String encodeRedirectURL(String url);
/**
* @param url
* the url to be encoded.
* @return the encoded URL if encoding is needed; the unchanged URL
* otherwise.
* @deprecated As of version 2.1, use encodeURL(String url) instead
*/
@Deprecated
public String encodeUrl(String url);
/**
* @param url
* the url to be encoded.
* @return the encoded URL if encoding is needed; the unchanged URL
* otherwise.
* @deprecated As of version 2.1, use encodeRedirectURL(String url) instead
*/
@Deprecated
public String encodeRedirectUrl(String url);
/**
* Sends an error response to the client using the specified status code and
* clears the output buffer. The server defaults to creating the response to
* look like an HTML-formatted server error page containing the specified
* message, setting the content type to "text/html", leaving cookies and
* other headers unmodified. If an error-page declaration has been made for
* the web application corresponding to the status code passed in, it will
* be served back in preference to the suggested msg parameter.
* <p>
* If the response has already been committed, this method throws an
* IllegalStateException. After using this method, the response should be
* considered to be committed and should not be written to.
*
* @param sc
* the error status code
* @param msg
* the descriptive message
* @exception IOException
* If an input or output exception occurs
* @exception IllegalStateException
* If the response was committed
*/
public void sendError(int sc, String msg) throws IOException;
/**
* Sends an error response to the client using the specified status code and
* clears the buffer. This is equivalent to calling {@link #sendError(int,
* String)} with the same status code and <code>null</code> for the message.
*
* @param sc
* the error status code
* @exception IOException
* If an input or output exception occurs
* @exception IllegalStateException
* If the response was committed before this method call
*/
public void sendError(int sc) throws IOException;
/**
* Sends a temporary redirect response to the client using the specified
* redirect location URL. This method can accept relative URLs; the servlet
* container must convert the relative URL to an absolute URL before sending
* the response to the client. If the location is relative without a leading
* '/' the container interprets it as relative to the current request URI.
* If the location is relative with a leading '/' the container interprets
* it as relative to the servlet container root.
* <p>
* If the response has already been committed, this method throws an
* IllegalStateException. After using this method, the response should be
* considered to be committed and should not be written to.
*
* @param location
* the redirect location URL
* @exception IOException
* If an input or output exception occurs
* @exception IllegalStateException
* If the response was committed or if a partial URL is given
* and cannot be converted into a valid URL
*/
public void sendRedirect(String location) throws IOException;
/**
* Sets a response header with the given name and date-value. The date is
* specified in terms of milliseconds since the epoch. If the header had
* already been set, the new value overwrites the previous one. The
* <code>containsHeader</code> method can be used to test for the presence
* of a header before setting its value.
*
* @param name
* the name of the header to set
* @param date
* the assigned date value
* @see #containsHeader
* @see #addDateHeader
*/
public void setDateHeader(String name, long date);
/**
* Adds a response header with the given name and date-value. The date is
* specified in terms of milliseconds since the epoch. This method allows
* response headers to have multiple values.
*
* @param name
* the name of the header to set
* @param date
* the additional date value
* @see #setDateHeader
*/
public void addDateHeader(String name, long date);
/**
* Sets a response header with the given name and value. If the header had
* already been set, the new value overwrites the previous one. The
* <code>containsHeader</code> method can be used to test for the presence
* of a header before setting its value.
*
* @param name
* the name of the header
* @param value
* the header value If it contains octet string, it should be
* encoded according to RFC 2047
* (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2047.txt)
* @see #containsHeader
* @see #addHeader
*/
public void setHeader(String name, String value);
/**
* Adds a response header with the given name and value. This method allows
* response headers to have multiple values.
*
* @param name
* the name of the header
* @param value
* the additional header value If it contains octet string, it
* should be encoded according to RFC 2047
* (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2047.txt)
* @see #setHeader
*/
public void addHeader(String name, String value);
/**
* Sets a response header with the given name and integer value. If the
* header had already been set, the new value overwrites the previous one.
* The <code>containsHeader</code> method can be used to test for the
* presence of a header before setting its value.
*
* @param name
* the name of the header
* @param value
* the assigned integer value
* @see #containsHeader
* @see #addIntHeader
*/
public void setIntHeader(String name, int value);
/**
* Adds a response header with the given name and integer value. This method
* allows response headers to have multiple values.
*
* @param name
* the name of the header
* @param value
* the assigned integer value
* @see #setIntHeader
*/
public void addIntHeader(String name, int value);
/**
* Sets the status code for this response. This method is used to set the
* return status code when there is no error (for example, for the status
* codes SC_OK or SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY). If there is an error, and the
* caller wishes to invoke an error-page defined in the web application, the
* <code>sendError</code> method should be used instead.
* <p>
* The container clears the buffer and sets the Location header, preserving
* cookies and other headers.
*
* @param sc
* the status code
* @see #sendError
*/
public void setStatus(int sc);
/**
* Sets the status code and message for this response.
*
* @param sc
* the status code
* @param sm
* the status message
* @deprecated As of version 2.1, due to ambiguous meaning of the message
* parameter. To set a status code use
* <code>setStatus(int)</code>, to send an error with a
* description use <code>sendError(int, String)</code>.
*/
@Deprecated
public void setStatus(int sc, String sm);
/**
* Get the HTTP status code for this Response.
*
* @return The HTTP status code for this Response
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public int getStatus();
/**
* Return the value for the specified header, or <code>null</code> if this
* header has not been set. If more than one value was added for this
* name, only the first is returned; use {@link #getHeaders(String)} to
* retrieve all of them.
*
* @param name Header name to look up
*
* @return The first value for the specified header. This is the raw value
* so if multiple values are specified in the first header then they
* will be returned as a single header value .
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public String getHeader(String name);
/**
* Return a Collection of all the header values associated with the
* specified header name.
*
* @param name Header name to look up
*
* @return The values for the specified header. These are the raw values so
* if multiple values are specified in a single header that will be
* returned as a single header value.
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public Collection<String> getHeaders(String name);
/**
* Get the header names set for this HTTP response.
*
* @return The header names set for this HTTP response.
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public Collection<String> getHeaderNames();
/**
* Configure the supplier of the trailer headers. The supplier will be
* called in the scope of the thread that completes the response.
* <br>
* Trailers that don't meet the requirements of RFC 7230, section 4.1.2 will
* be ignored.
* <br>
* The default implementation is a NO-OP.
*
* @param supplier The supplier for the trailer headers
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if this method is called when the
* underlying protocol does not support trailer headers or if using
* HTTP/1.1 and the response has already been committed
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public default void setTrailerFields(Supplier<Map<String, String>> supplier) {
// NO-OP
}
/**
* Obtain the supplier of the trailer headers.
* <br>
* The default implementation returns null.
*
* @return The supplier for the trailer headers
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public default Supplier<Map<String, String>> getTrailerFields() {
return null;
}
/*
* Server status codes; see RFC 7231.
*/
/**
* Status code (100) indicating the client can continue.
*/
public static final int SC_CONTINUE = 100;
/**
* Status code (101) indicating the server is switching protocols according
* to Upgrade header.
*/
public static final int SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101;
/**
* Status code (200) indicating the request succeeded normally.
*/
public static final int SC_OK = 200;
/**
* Status code (201) indicating the request succeeded and created a new
* resource on the server.
*/
public static final int SC_CREATED = 201;
/**
* Status code (202) indicating that a request was accepted for processing,
* but was not completed.
*/
public static final int SC_ACCEPTED = 202;
/**
* Status code (203) indicating that the meta information presented by the
* client did not originate from the server.
*/
public static final int SC_NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203;
/**
* Status code (204) indicating that the request succeeded but that there
* was no new information to return.
*/
public static final int SC_NO_CONTENT = 204;
/**
* Status code (205) indicating that the agent <em>SHOULD</em> reset the
* document view which caused the request to be sent.
*/
public static final int SC_RESET_CONTENT = 205;
/**
* Status code (206) indicating that the server has fulfilled the partial
* GET request for the resource.
*/
public static final int SC_PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206;
/**
* Status code (300) indicating that the requested resource corresponds to
* any one of a set of representations, each with its own specific location.
*/
public static final int SC_MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300;
/**
* Status code (301) indicating that the resource has permanently moved to a
* new location, and that future references should use a new URI with their
* requests.
*/
public static final int SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301;
/**
* Status code (302) indicating that the resource has temporarily moved to
* another location, but that future references should still use the
* original URI to access the resource. This definition is being retained
* for backwards compatibility. SC_FOUND is now the preferred definition.
*/
public static final int SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302;
/**
* Status code (302) indicating that the resource reside temporarily under a
* different URI. Since the redirection might be altered on occasion, the
* client should continue to use the Request-URI for future
* requests.(HTTP/1.1) To represent the status code (302), it is recommended
* to use this variable.
*/
public static final int SC_FOUND = 302;
/**
* Status code (303) indicating that the response to the request can be
* found under a different URI.
*/
public static final int SC_SEE_OTHER = 303;
/**
* Status code (304) indicating that a conditional GET operation found that
* the resource was available and not modified.
*/
public static final int SC_NOT_MODIFIED = 304;
/**
* Status code (305) indicating that the requested resource <em>MUST</em> be
* accessed through the proxy given by the <code><em>Location</em></code>
* field.
*/
public static final int SC_USE_PROXY = 305;
/**
* Status code (307) indicating that the requested resource resides
* temporarily under a different URI. The temporary URI <em>SHOULD</em> be
* given by the <code><em>Location</em></code> field in the response.
*/
public static final int SC_TEMPORARY_REDIRECT = 307;
/**
* Status code (400) indicating the request sent by the client was
* syntactically incorrect.
*/
public static final int SC_BAD_REQUEST = 400;
/**
* Status code (401) indicating that the request requires HTTP
* authentication.
*/
public static final int SC_UNAUTHORIZED = 401;
/**
* Status code (402) reserved for future use.
*/
public static final int SC_PAYMENT_REQUIRED = 402;
/**
* Status code (403) indicating the server understood the request but
* refused to fulfill it.
*/
public static final int SC_FORBIDDEN = 403;
/**
* Status code (404) indicating that the requested resource is not
* available.
*/
public static final int SC_NOT_FOUND = 404;
/**
* Status code (405) indicating that the method specified in the
* <code><em>Request-Line</em></code> is not allowed for the resource
* identified by the <code><em>Request-URI</em></code>.
*/
public static final int SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405;
/**
* Status code (406) indicating that the resource identified by the request
* is only capable of generating response entities which have content
* characteristics not acceptable according to the accept headers sent in
* the request.
*/
public static final int SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE = 406;
/**
* Status code (407) indicating that the client <em>MUST</em> first
* authenticate itself with the proxy.
*/
public static final int SC_PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED = 407;
/**
* Status code (408) indicating that the client did not produce a request
* within the time that the server was prepared to wait.
*/
public static final int SC_REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 408;
/**
* Status code (409) indicating that the request could not be completed due
* to a conflict with the current state of the resource.
*/
public static final int SC_CONFLICT = 409;
/**
* Status code (410) indicating that the resource is no longer available at
* the server and no forwarding address is known. This condition
* <em>SHOULD</em> be considered permanent.
*/
public static final int SC_GONE = 410;
/**
* Status code (411) indicating that the request cannot be handled without a
* defined <code><em>Content-Length</em></code>.
*/
public static final int SC_LENGTH_REQUIRED = 411;
/**
* Status code (412) indicating that the precondition given in one or more
* of the request-header fields evaluated to false when it was tested on the
* server.
*/
public static final int SC_PRECONDITION_FAILED = 412;
/**
* Status code (413) indicating that the server is refusing to process the
* request because the request entity is larger than the server is willing
* or able to process.
*/
public static final int SC_REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE = 413;
/**
* Status code (414) indicating that the server is refusing to service the
* request because the <code><em>Request-URI</em></code> is longer than the
* server is willing to interpret.
*/
public static final int SC_REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG = 414;
/**
* Status code (415) indicating that the server is refusing to service the
* request because the entity of the request is in a format not supported by
* the requested resource for the requested method.
*/
public static final int SC_UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE = 415;
/**
* Status code (416) indicating that the server cannot serve the requested
* byte range.
*/
public static final int SC_REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE = 416;
/**
* Status code (417) indicating that the server could not meet the
* expectation given in the Expect request header.
*/
public static final int SC_EXPECTATION_FAILED = 417;
/**
* Status code (500) indicating an error inside the HTTP server which
* prevented it from fulfilling the request.
*/
public static final int SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500;
/**
* Status code (501) indicating the HTTP server does not support the
* functionality needed to fulfill the request.
*/
public static final int SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 501;
/**
* Status code (502) indicating that the HTTP server received an invalid
* response from a server it consulted when acting as a proxy or gateway.
*/
public static final int SC_BAD_GATEWAY = 502;
/**
* Status code (503) indicating that the HTTP server is temporarily
* overloaded, and unable to handle the request.
*/
public static final int SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = 503;
/**
* Status code (504) indicating that the server did not receive a timely
* response from the upstream server while acting as a gateway or proxy.
*/
public static final int SC_GATEWAY_TIMEOUT = 504;
/**
* Status code (505) indicating that the server does not support or refuses
* to support the HTTP protocol version that was used in the request
* message.
*/
public static final int SC_HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 505;
}
2. Response header
1) response.setHeader("이름","값");
response.setHeader("content-Type","text/plan;charset=utf-8"); //컨텐츠 타입
response.setHeader("Cache-Control","no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate"); //캐쉬 무효화
response.setHeader("Pragma","no-cache"); //과거 캐쉬 무효화
response.setHeader("my-header","hello"); //원하는 임의의 값을 넣을 수 있음.2) 편의 메서드
response.setContentType("text/plain");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentLength(2); //(생략시 자동 생성)
3. Cookie ( Response header )
Set-Cookie: myCookie=good; Max-Age=600; 쿠키 유효 시간 600
1) response.setHeader("이름","값");
response.setHeader("Set-Cookie", "myCookie=good; Max-Age=600");
2) Cookie 클래스
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("myCookie", "good");
cookie.setMaxAge(600); //600초
response.addCookie(cookie);
4. Redirect ( Response header )
Status Code 302
Location: /basic/hello-form.html
1) response.setHeader("이름","값");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FOUND); //302
response.setHeader("Location", "/basic/hello-form.html");
2) 편의 메서드
response.sendRedirect("이동 경로");
response.sendRedirect("/basic/hello-form.html");
4. 응답 데이터
1) 단순 텍스트 응답
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("ok");
2) HTML 응답
//1. 컨텐츠 타입
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//2. html 출력
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("<html>");
writer.println("<body>");
writer.println("<div>html 전달합니다.</div>");
writer.println("</body>");
writer.println("</html>");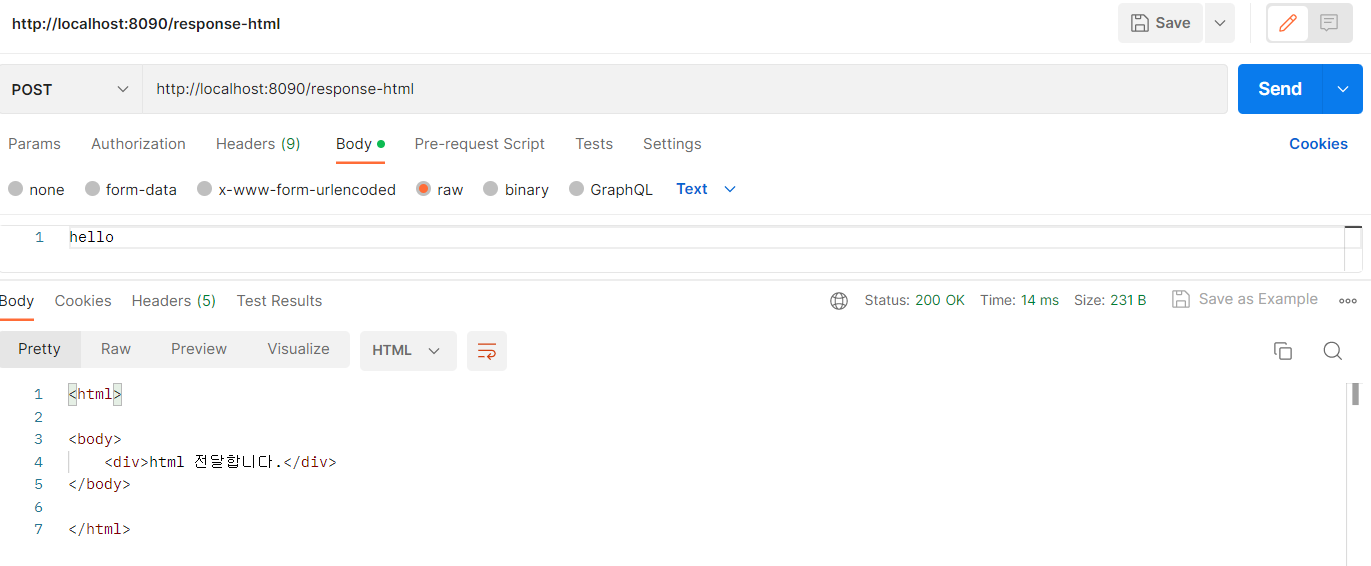
3) HTTP API - JSON 응답
//1. 컨텐츠 타입
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//2. 전달할 객체 생성
HelloData helloData = new HelloData();
helloData.setUsername("lee");
helloData.setAge(10);
//3-1. json 형태로 변환하려면 ObjectMapper가 필요하다.
//3-2. json 형태로 변환 {"username":"lee","age":10}
String result = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(helloData);
//4. 클라이언트 전달
response.getWriter().write(result);//3-1. json 형태로 변환하려면 ObjectMapper가 필요하다.
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();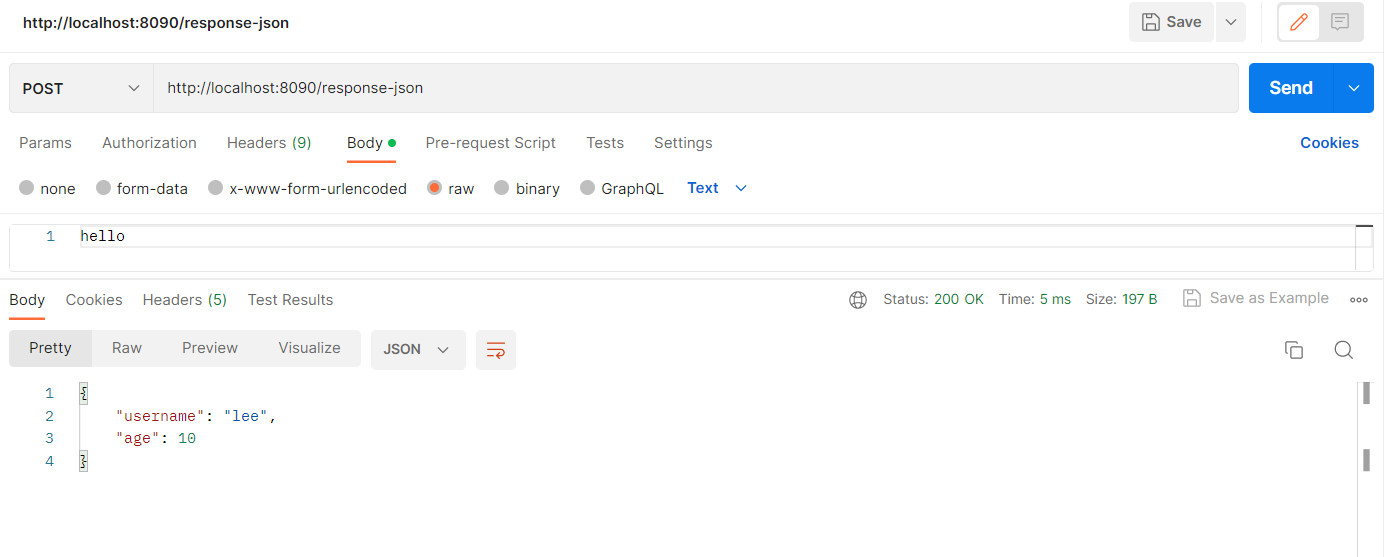
728x90
'BackEnd > Servlet · JSP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ Servlet&JSP ] HttpServletRequest 기능 (0) | 2023.03.21 |
|---|---|
| [ Servlet&JSP ] HTTP 요청 데이터 GET · POST · HTTP message body (1) | 2023.03.20 |
| [ Servlet / JSP ] Model 1 방식과 Model 2 방식 비교 (0) | 2023.02.22 |
| [ Project / Servlet · JSP ] 1차 과제 Model 2 방식 - (2) 게시판 만들기 ( 검색 기능 ) (0) | 2023.02.16 |
| [ Project / Servlet · JSP ] 1차 과제 Model 2 방식 - (1) 게시판 만들기 ( 페이징 버튼 기능 ) (0) | 2023.02.15 |
